
Karplus-Strong synthesis
卡普拉斯-斯特朗合成/Ka3 Pu3 La1 Si1-Si1 Te4 Lang3 He2 Cheng2
n/a
CHEARS: False
EARS: False
CMT: True
EARS2 Encyclopedia: False
CHEARS:
源自《计算机音乐教程》、科蒂斯·罗兹、人民音乐出版社、2011。
The Karplus-Strong (KS) algorithm for plucked string and drum synthesis is an efficient technique based on the principle of a delay line or recirculating wavetable (Karplus and Strong 1983; Jaffe and Smith 1983). The computational resources needed for basic KS synthesis are modest (no multiplications necessary). So it is not surprising that the technique has been implemented on hardware ranging from a slow 8-bit microprocessor to a large digital synthesizer (Karplus and Strong 1983).
Plucked Strings
The basic KS algorithm starts with a wavetable of length p filled with random values. As values are read out of the wavetable from the right (figure 7.12), they are modified in some way, and the result is reinserted at the left of the wavetable. The simplest modification is an averaging of the current sample with the previous sample - the core operation of a simple lowpass filter.
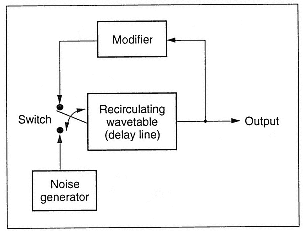
Figure 7.12
Core of the Karplus-Strong recirculating wavetable. The input to the recirculating wavetable switches to the noise source at the beginning of each event, then switches back to the modifier loop for the rest of the event. The modifier averages successive samples, simulating a damping effect.
Drumlike Timbres
KS generates drumlike timbres by using a slightly more complicated modifier to the fedback sample. The timbre is controlled by setting the value of a probability parameter b called the blend factor.
(Source: Curtis Roads, The Computer Music Tutorial, The MIT Press 1996)
EARS:
EARS 2:
参看其它/See Also
术语翻译/Terms Translator
术语校对/Terms Proofreader
术语顾问/Consultant to terminology
参考文献/Bibliography
讲座/Lecture
评论/Comments
发表评论(预先注册)/Add comment on this term(members ONLY)